Press 'o' to toggle the slide overview and 'f' for full-screen mode.
Choose the theme in which to view this presentation:Black - White - League - Sky - Beige - Simple
Serif - Blood - Night - Moon - Solarized
Copyright © John Lindsay, 2015
GEOG*2420
The Earth From Space
Airborne and Spaceborne
Imaging Systems Part 1
John Lindsay
Fall 2015
Readings
Jensen Chapter 4 pg. 91-104
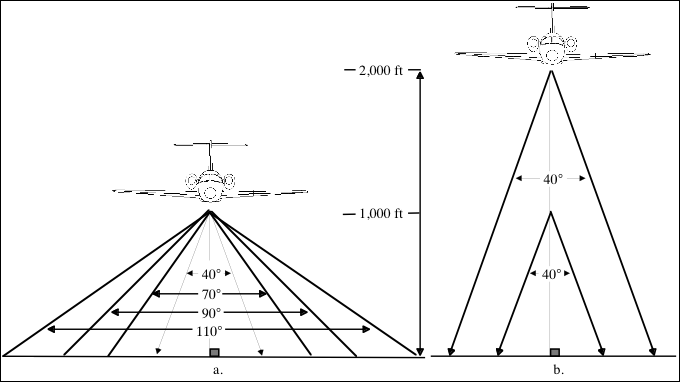
Camera lens angle and flying height determine the field of view
Aerial Photography
- Vantage Points
- Aerial Camera Features
- Aerial Camera Types
Vantage Points
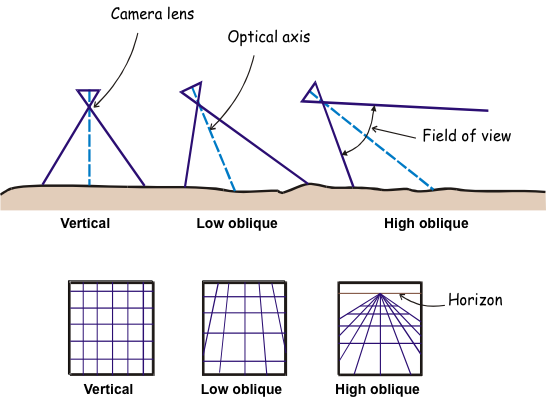
Vantage Points
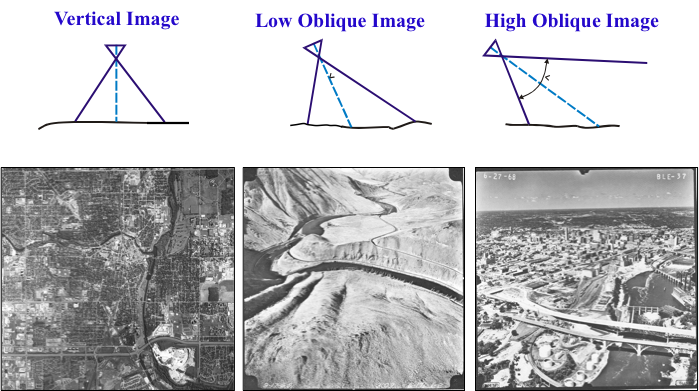
Vertical Aerial Photography
- Main vantage point used for planimetric and topographic maps, digital
elevation model (DEM) creation, and
orthophotos (image maps)
Oblique Aerial Photography
- People are generally better at interpreting oblique images because the side-view is what we're used to...we have plenty of experience.
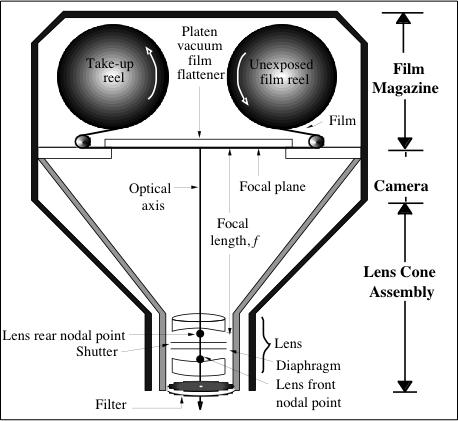
Aerial Camera Features
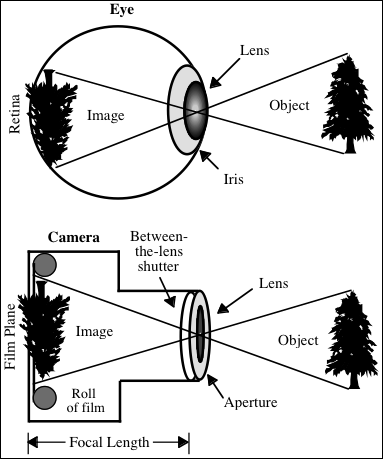
- A comparison of eye and camera optical components
Aerial Camera Features
Focal plane : the area in which the film is held flat during an exposure.Focal length (f): the distance from the lens to the focal plane.- Cameras used by photographers usually have zoom lenses, where f can be changed continuously.
- Cameras used for aerial photography usually have fixed focal lengths, e.g. 88 mm, 152 mm, 210 mm and 305 mm.
Aerial Camera Features
f/stop : The ratio of f to the diameter of the lens opening (d).- This is related to the amount of light admitted through the lens opening per unit of time.
- f/1 is said to be faster than f/10
Aerial Camera Features
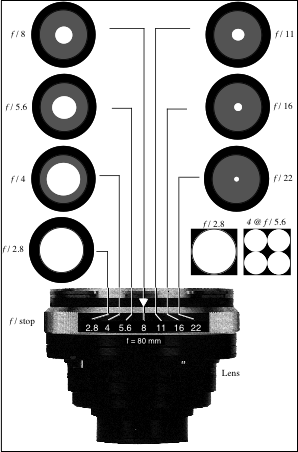
The f/stops for a camera lens and the size of the aperture openings
Aerial Camera Features
- Film emulsion requires the correct amount of light for an exposure.
- Must adjust the aperture size (f/stop) and the shutter speed.
Exposure time : the length of time that the shutter is open.- This relation can be difficult given that you also have to take into account the speed of the aircraft!
Aerial Camera Types
- Single-lens mapping (metric) cameras
- Multiple-lens (multi-band) cameras
- Digital cameras
Single-lens metric cameras
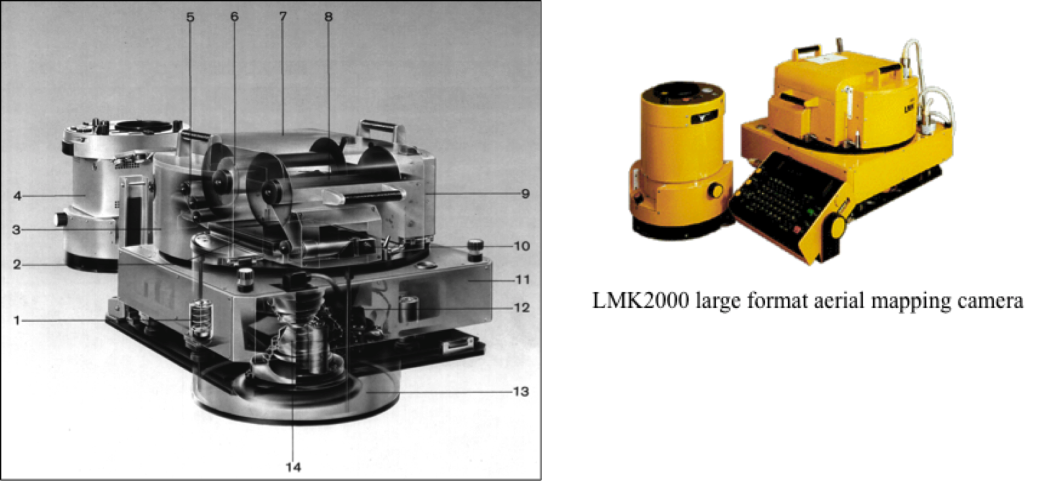
'Metric' cameras are calibrated to provide the highest geometric and radiometric quality
Single-lens metric cameras
- An intervalometer is used to expose the film at specific intervals of time.
Large Format vs. Small Format Cameras
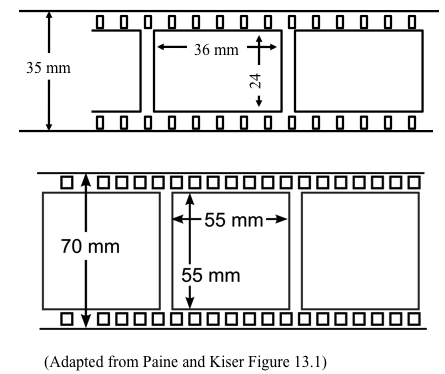
Large Format vs. Small Format Cameras
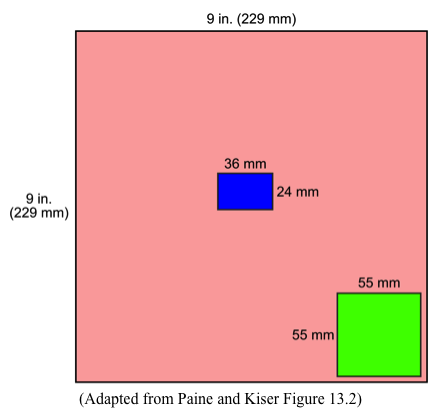
Large Format vs. Small Format Cameras
| Large Format | Small Format |
|---|---|
| Very expensive to buy and to process | Inexpensive |
| Calibrated | Usually uncalibrated but can buy calibrated SF cameras |
| Film is perfectly flat | Significant lens distortions |
| Greater variety of film, filters, and lenses | |
| Faster processing |

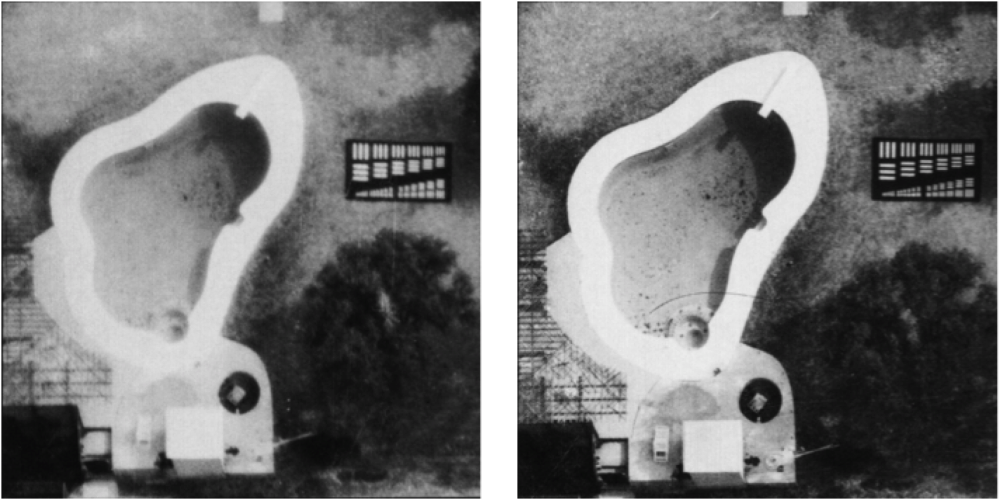
Forward Motion Compensation