How to select vector features
By John Lindsay (Last modified, Feb. 2014)
Selecting individual or groups of features from a vector file that meet some criteria is central to GIS. In Whitebox GAT, vector features can be selected directly using the Select Feature tool, based on their attributes, or based on their spatial relations with the features in another vector layer using the Isolate Vector Features By Location tool.
Direct Feature Selection
To directly select features within a vector layer, first add the layer to the current map and be sure that the layer is selected as the active map layer in the Layers tab. It will be highlighted in blue if it is the active map layer. Next select the Select Feature tool from the Whitebox toolbar or from within the View menu (see figure below).
When Whitebox is in Feature Selection mode, grey bounding boxes will be drawn over any polyline or polygon features as you move the mouse over the map area (see below). A central point, also drawn in light grey, will appear at the centre of the selection box. If the mouse is positioned in a location where the bounding boxes of more than one vector feature overlap, each of the selection boxes will be drawn. If you click the map area, the feature with the nearest selection box centre to the mouse location will be selected and will be drawn with a cyan coloured outline. Notice that the selection box will not appear for point vector features, but the same criterion of nearest feature location to the mouse location at the time of clicking the map area is used to determine which point is selected.
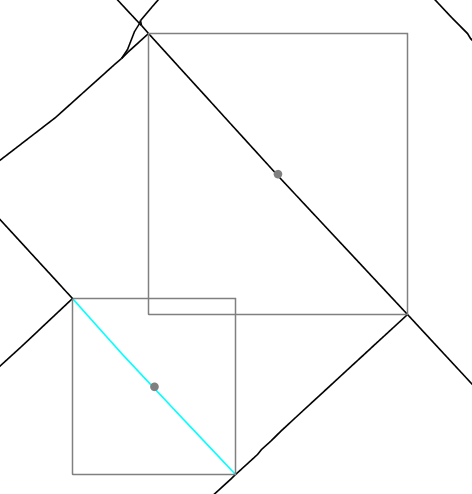
Clicking the map area and dragging the mouse will result in the selection of multiple features, including any feature for which the selection box centre point is within the drag box. The selected features will be added to the Features tab on the Whitebox side pane and you will be able to view the attributes of each selected feature. It is also possible to create a new shapefile containing only the selected features by choosing Save Selected Features In New Vector from the Data Layers tab. You will be asked to enter the name of the new vector and will be automatically displayed and set as the active map layer after creation.
Selection Based On Feature Attributes
To select features based on attributes contained with the attributes table, first be sure that the vector layer of interest is selected as the active map layer in the Layers tab. Now open the attribute table of the vector layer either by selecting the View Attribute Table icon located on the toolbar, or by selecting View Attribute Table from the Data Layers menu. Click on the Feature Selection tab (see below).
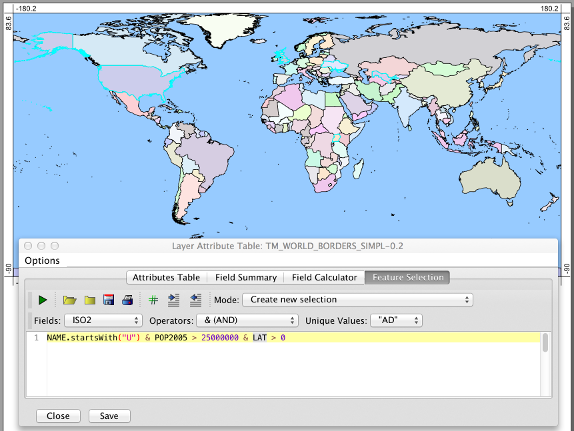
The first important feature of this tab pane is the Execute Code icon (green arrow) used to run a selection script. You will also notice a drop-down menu that can be used to specify the type of selection operation including the following four modes:
- Create new selection
- Add to current selection
- Remove from current selection
- Select from current selection
Each of the various modes differ in the way that the newly identified features are related to any features that are already selected. The default mode of Create new selection will simply ignore any existing selection and create a new selection set.
There is also a drop-down menu containing the names of each of the fields within the attribute table. If you select a field from the field name menu, the field name will automatically be inserted into the selection script text area. The selection script text area has an auto-complete feature that allows users to press Control (Ctrl) and the space bar after having typed one or a few letters of the field name and a helpful pop-up window will appear from which you can select the correct field name. This auto-complete feature is also available to help identify all of the methods that are associated with fields containing strings (e.g. 'startsWith', 'toLowerCase', 'equals', 'contains', etc.). If the selected field is a text string or is a numeric integer value with fewer than 300 unique values within the table, these values will appear listed in the 'Unique Values' drop-down value. Selecting a unique value will result in it being inserted into the selection script text area.
The operators drop-down menu provides a quick-link list to many of the commonly used operators. Importantly, the selection is based on Groovy-language scripting. Groovy is a super-set of the Java programming language and provides substantial power to the feature selection process. The common logical and comparison operators that are used in a selection script include:
- & (logical AND operator)
- | (logical OR operator)
- == (equal-to comparison operator for numeric data types; for text strings use str1.equals(str2) method)
- != (not-equal-to comparison operatorfor numeric data types; for text strings use !str1.equals(str2) method))
- > (greater-than comparison operator)
- >= (greater-than-equal-to comparison operator)
- < (greater-than comparison operator)
- <= (greater-than-equal-to comparison operator)
The selection script is typically a single line long, although multiline scripts are accepted as well. Importantly, the last line of the script must evaluate to a Boolean (true or false) value. Each row in the attribute table will be evaluated and if the final line expression evaluates to true, the corresponding feature will be selected. The values within each of the fields for a row are assigned to variables with the same name as the field (case sensitive). There is also an extra variable available within the script called 'index' which is the row (feature) number. For example, the following selection script:
index < 100
would select the first 100 features in the vector layer. Complex selections are also possible. For example,
NAME.startsWith("C") & POP2005 > 25000000 & LAT > 0.0
selects the features that have 'NAME' starting with the letter 'U', 'POP2005' greater than 25,000,000 and 'LAT' greater than 0.0. And,
CLASS.equals("agriculture") | CLASS.equals("forest")
selects all features that have an attribute CLASS value of either agriculture or forest.
After performing a selection, you will find that a filter has been applied to the attribute table such that only the selected features are displayed. The Options menu allows you to remove this filter, to copy the selected features to the clip board (they can then be pasted into a spreadsheet program as comma-separated values (CSV) text), or even save the features as a separate vector layer. The selected features will also be rendered on the map with a cyan coloured outline.